Prepare OSGeoLive for Spatial Ecology courses
In order to execute the Spatial Ecology exercise we will need first install the OSGeoLive Linux Virtual Machine and then populate with additional software and data.
OSGeoLive is a self-contained bootable DVD, USB thumb drive or Virtual Machine based on Lubuntu, that allows you to try a wide variety of open source geospatial software without installing anything. It is composed entirely of free software, allowing it to be freely distributed, duplicated and passed around (source https://live.osgeo.org/en/index.html)
You can follow the below instructions, moreover the OSGeoLive installation YouTube video can guide along the full procedure. Pay attention that the video is base on the Osgeolive 13 version, so some differences can be present comparing with the current version.
Software requirements
For running a Virtual Machine in your OS we need a virtualization software such as Virtualbox and a vmdk file that contains the virtualized OS.
Hardware requirements
Hard disk
Be sure to have at least 60 GIGA of free space in your hard disk before to start the VM installation procedure. Avoid the use of USB-external-hard-disk, due that the USB connection will slow down the VM performance.
RAM
Be sure that your computer have at lest 8 GIGA ram (more better). Indeed with the VM running and the zoom session open for following the lecture the 8GIGA will be barely on the limit.
Install Virtualbox
Open you browser and go to https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads and base on your OS download the Virtualbox executable and install it.
Install OSGeoLive
Download OSGeoLive
Open you browser and go to https://download.osgeo.org/livedvd/releases/16.0/ and proceed to download the osgeolive-??.0-amd64.vmdk.7z. At the time of writing the last version is 16 so vmdk file is osgeolive-16.0-amd64.vmdk.7z. The osgeolive-16.0-amd64.vmdk.7z is a quite large file therefore according to your Internet connection it can take several hours. When the download is finished unzipped using 7zip. Mac users can use The Unarchiver for unzip the osgeolive-16.0-amd64.vmdk.7z. A this point you are ready to load the osgeolive-16.0-amd64.vmdk inside Virtualbox.
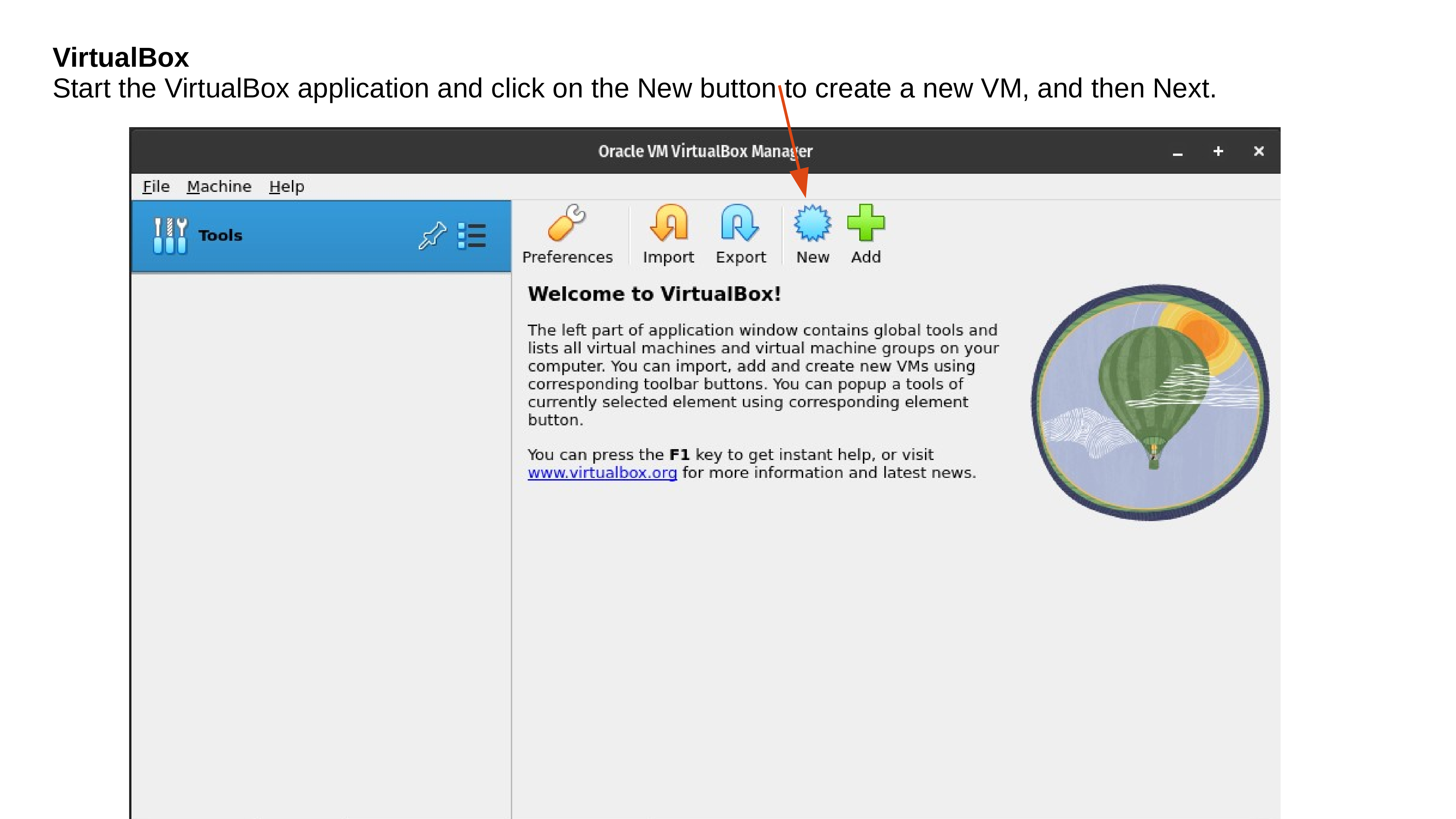
Install OSGeoLive inside Virtualbox
Lunch Virtualbox from OS and follow the below instructions.

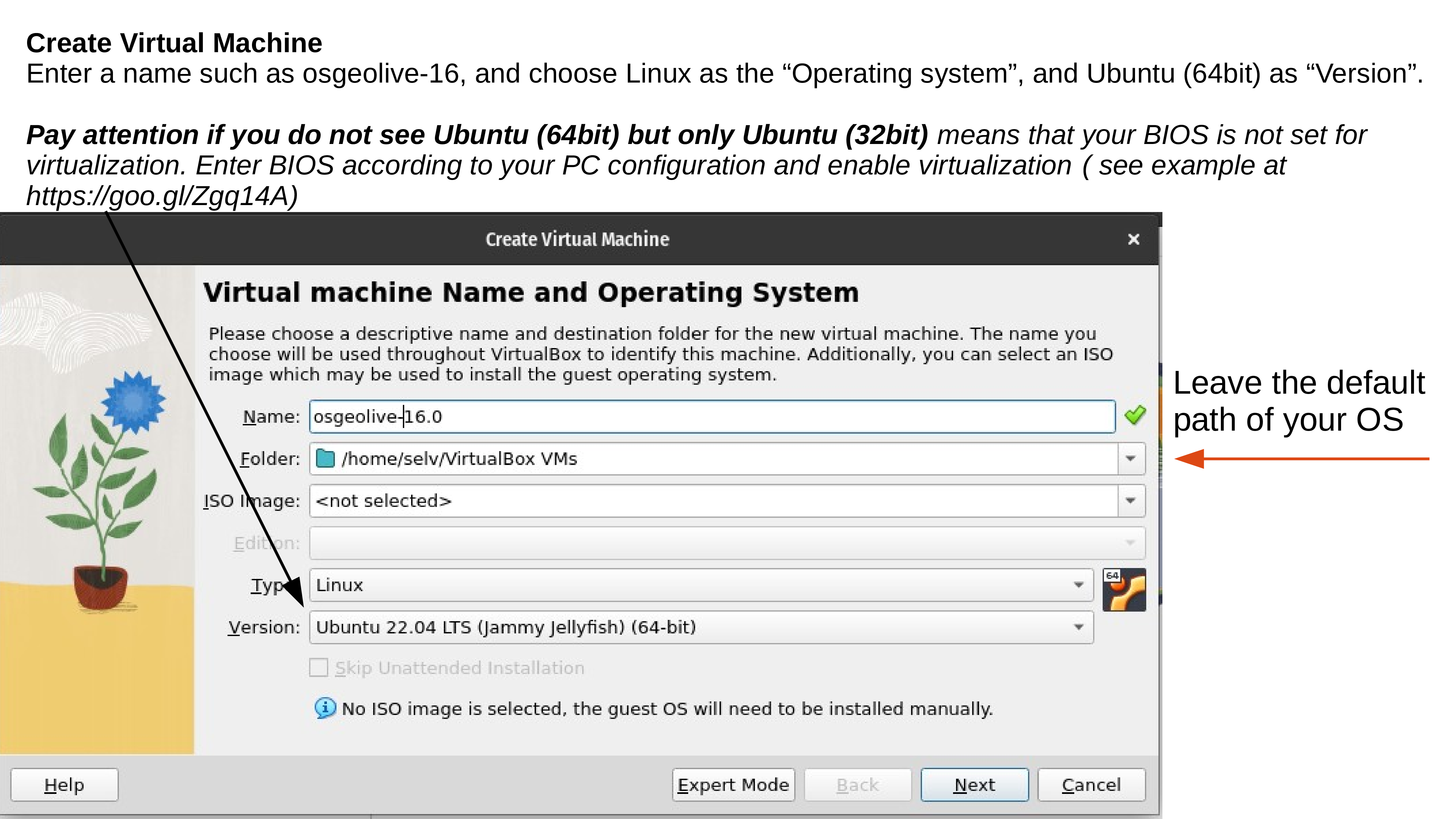
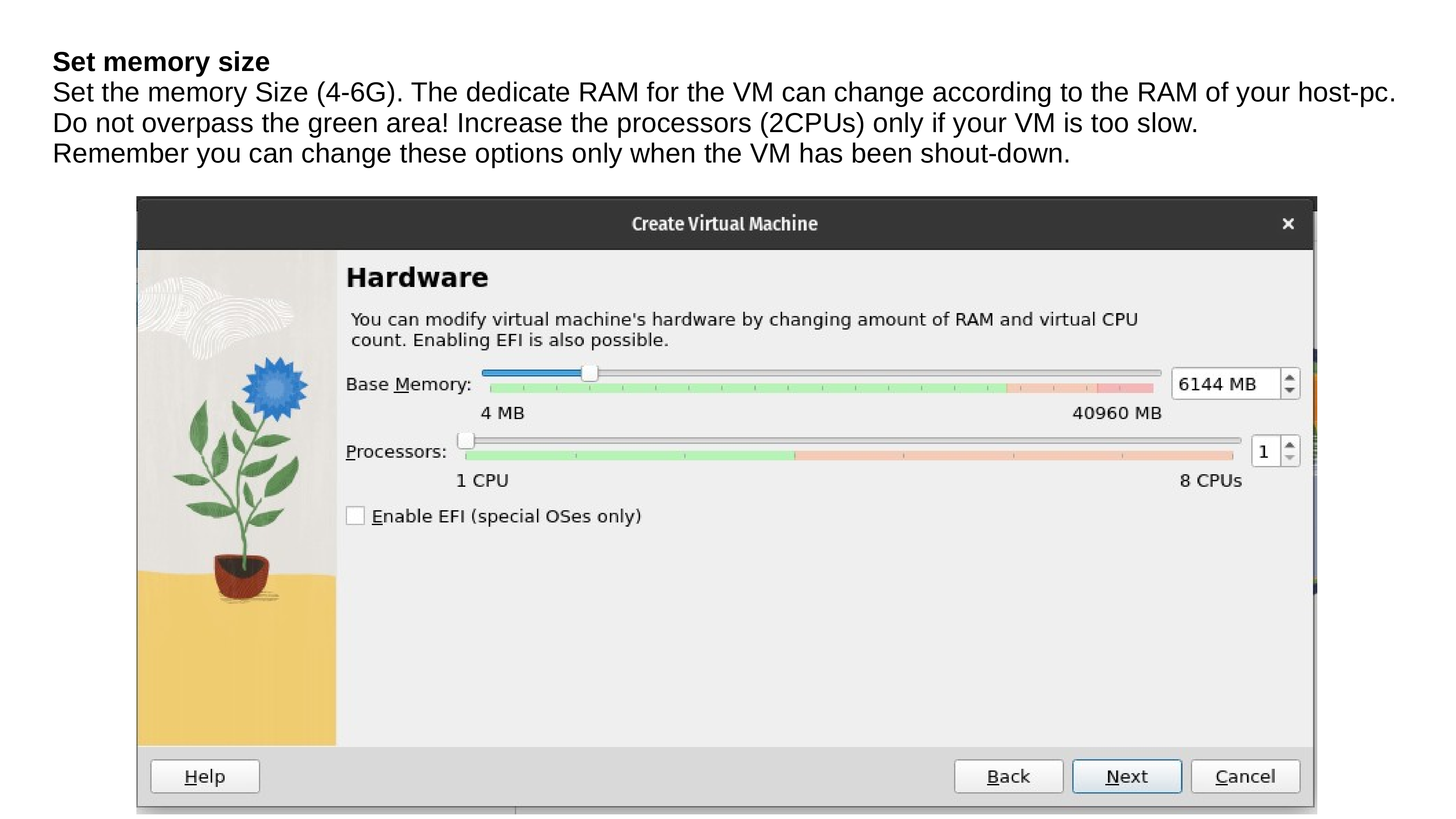
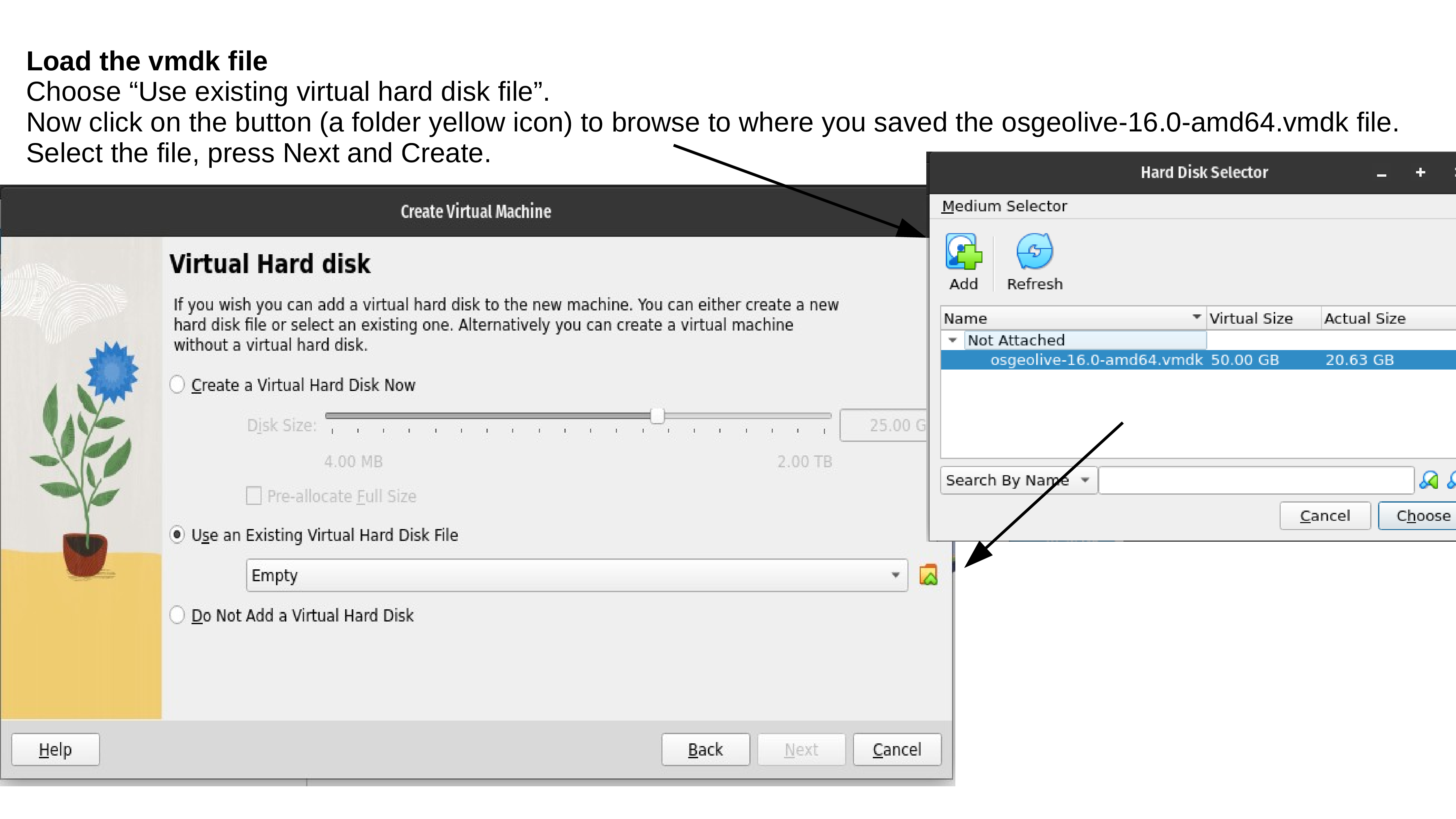
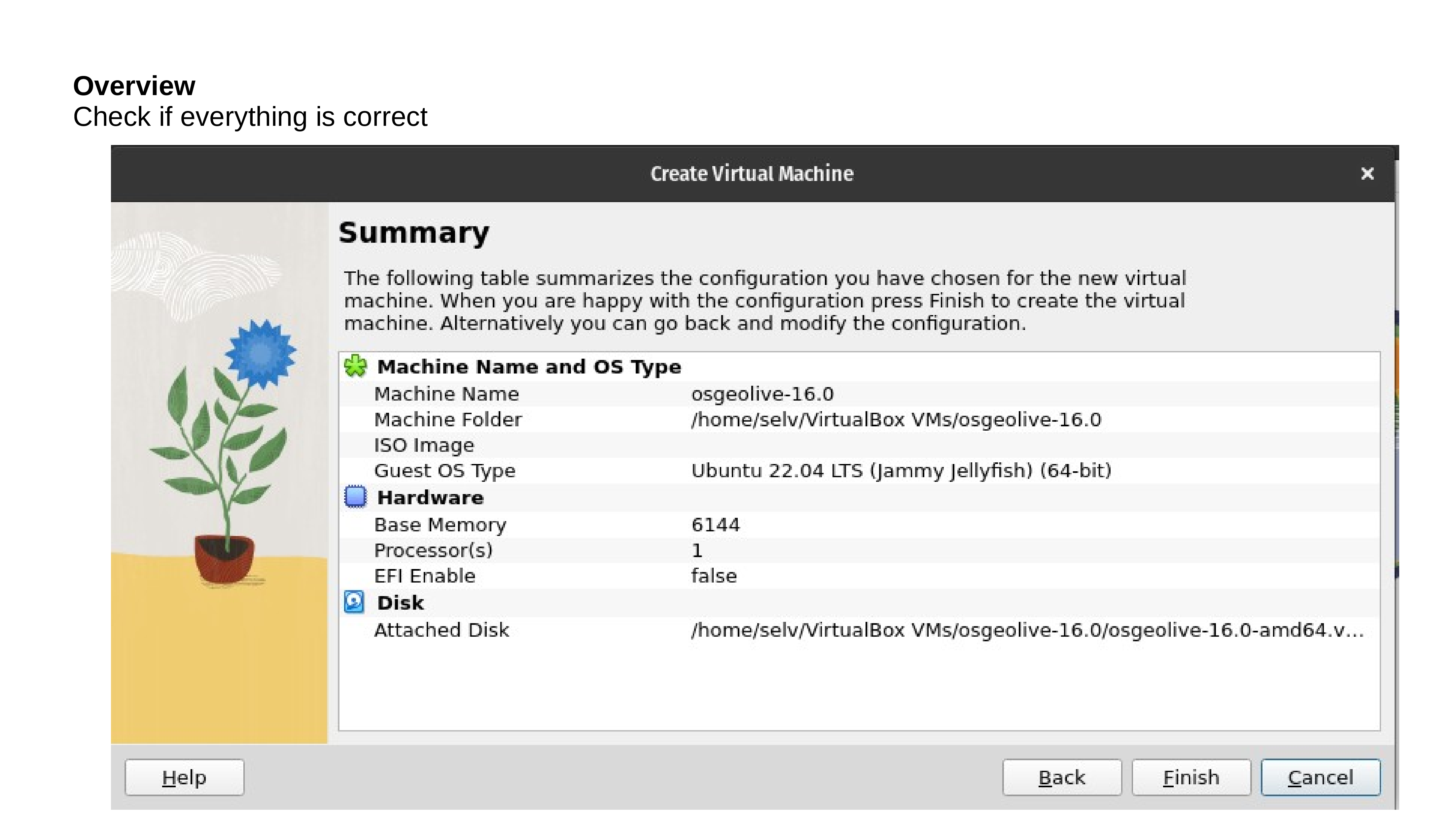
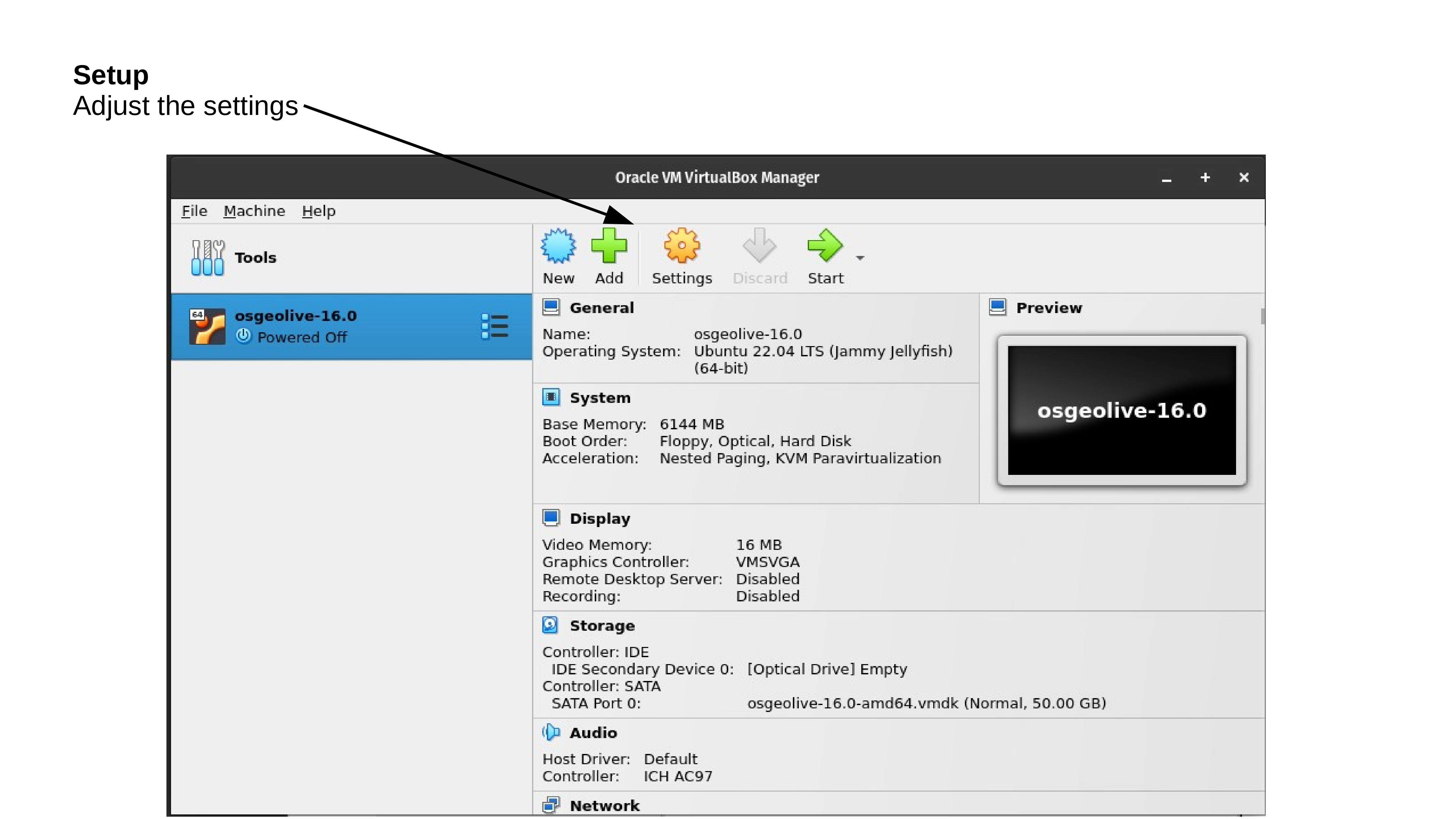
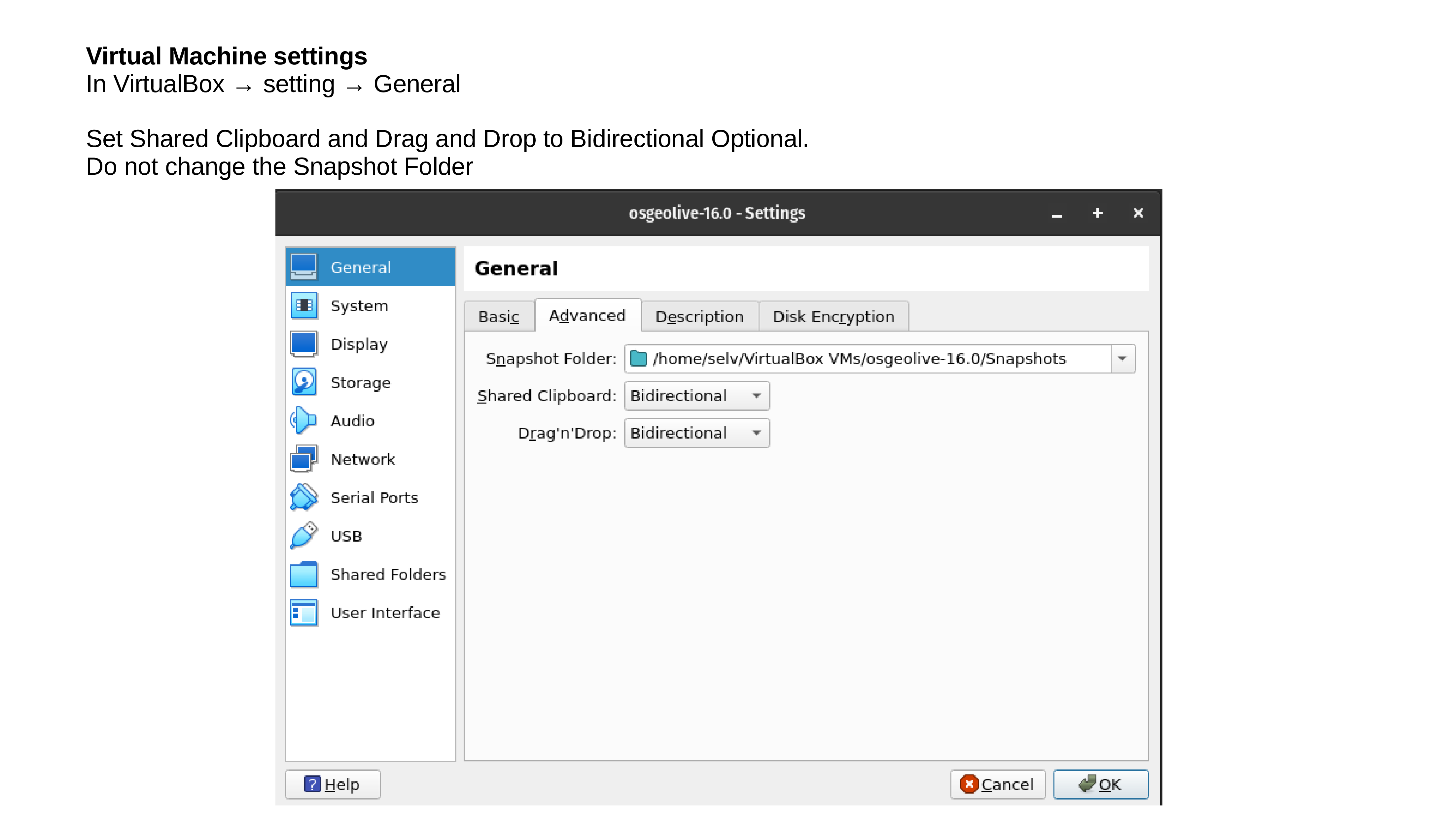
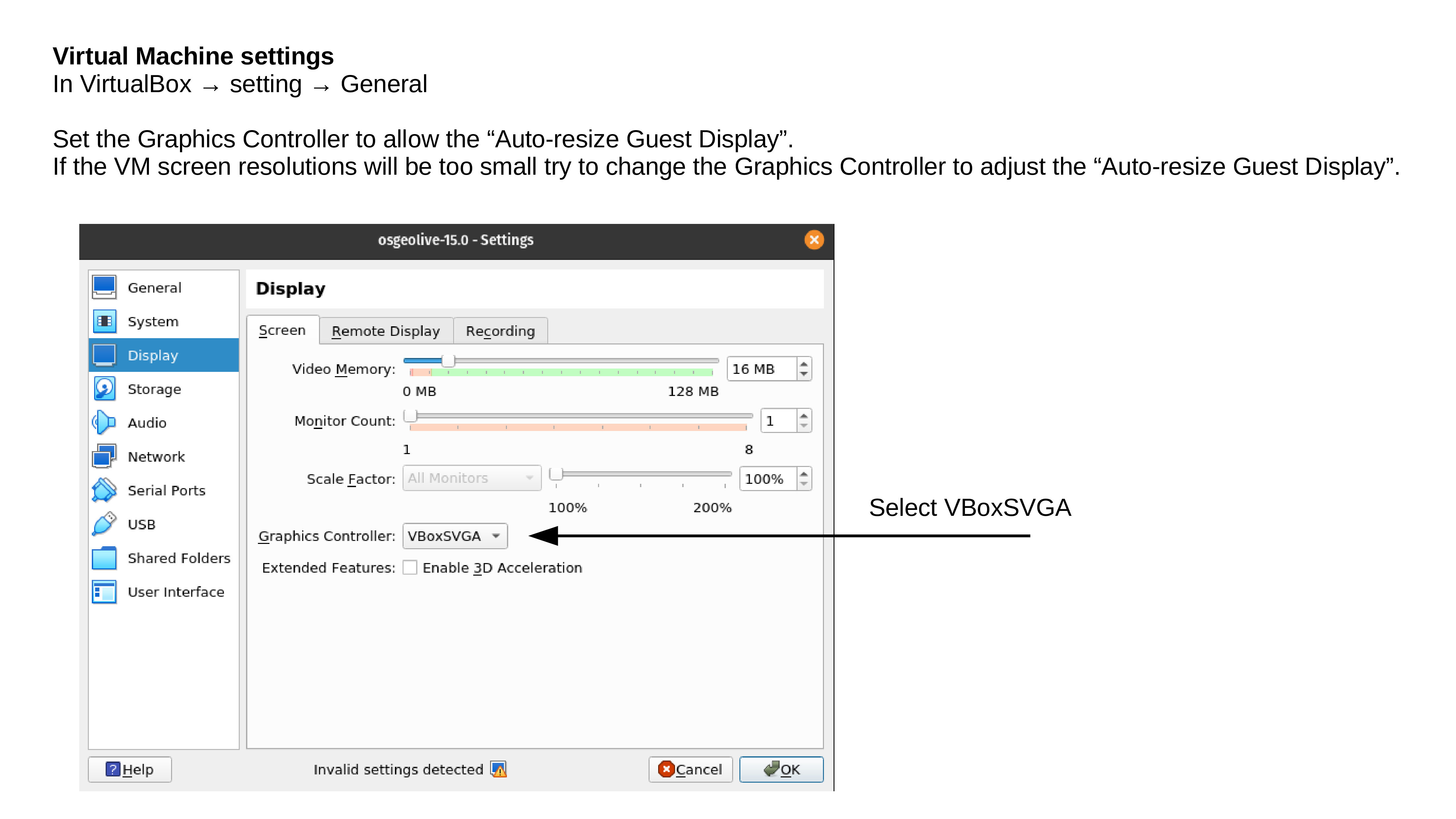
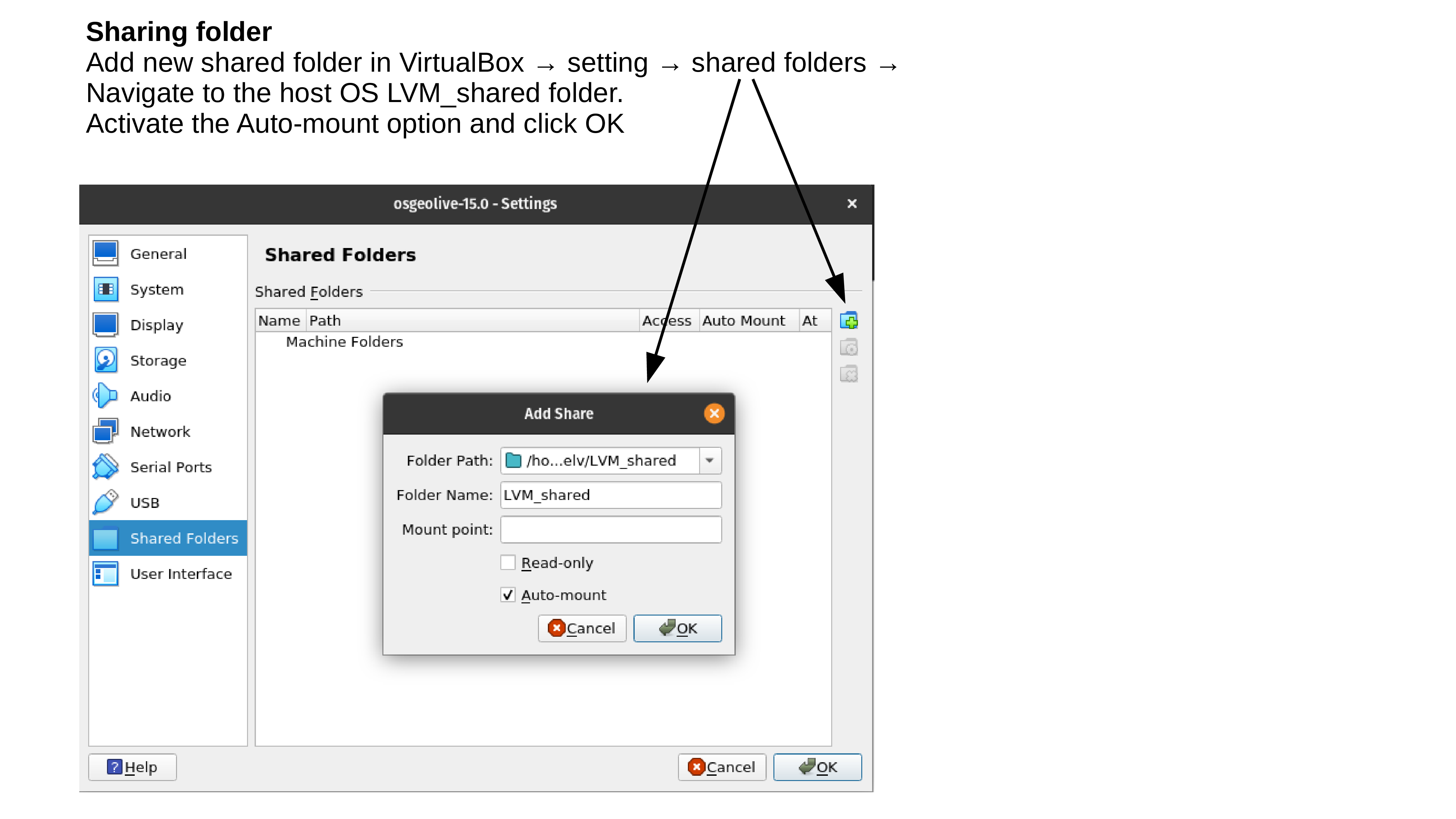
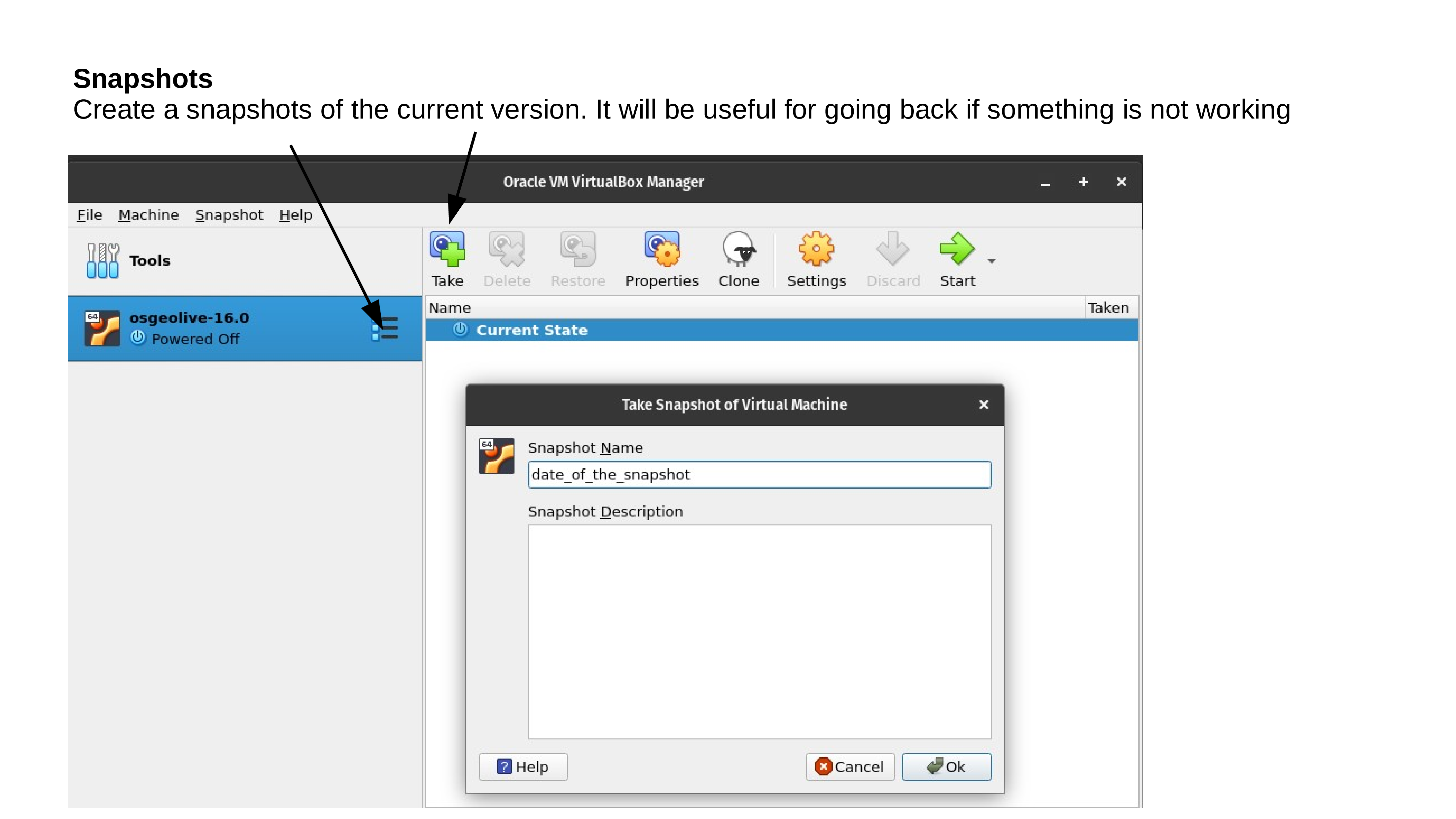
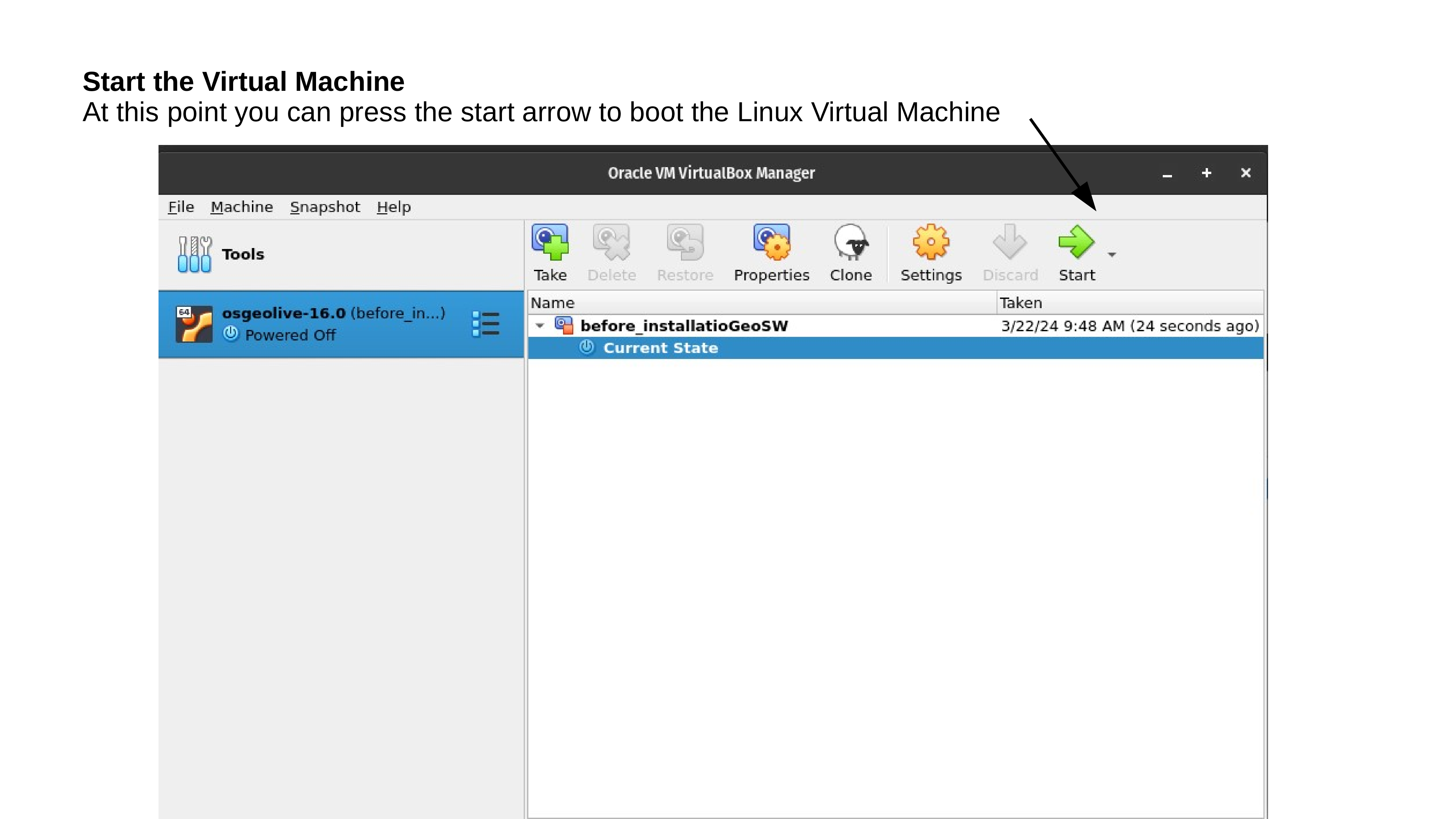
Test your OSGeoLive Virtual Machine
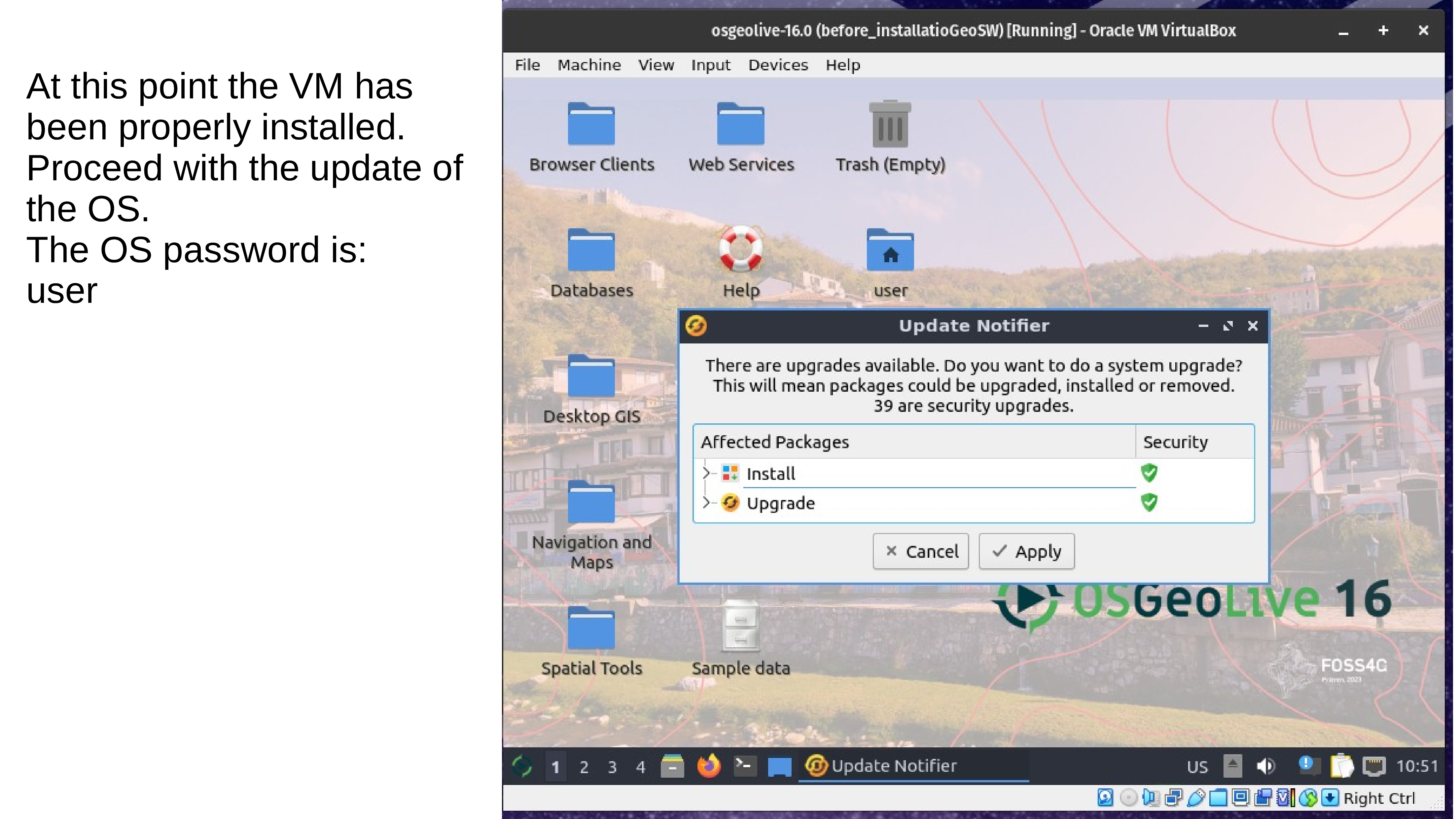
If you follow all the steps correctly the OSGeoLive Virtual Machine you should pop-up in the Virtual Box window showing something like this:
If the OSGeoLive start with a black screen with a “kernel panic message” means that there are still some settings that are not allowing the virtualization. This page is a good tutorial for solving the issues in Windows-10 and this one for Windows-11.
Setting you keyboard layout
If are not use the US keyboard you have to add your keyboard layout to the bottom menubar. Therefore on the left bottom corner write “keyboard” in the search box, and select Keyboard and Mouse.

Then select “Keyboard Layout” > “Add” and select your keyboard layout in accordance to your country and language.
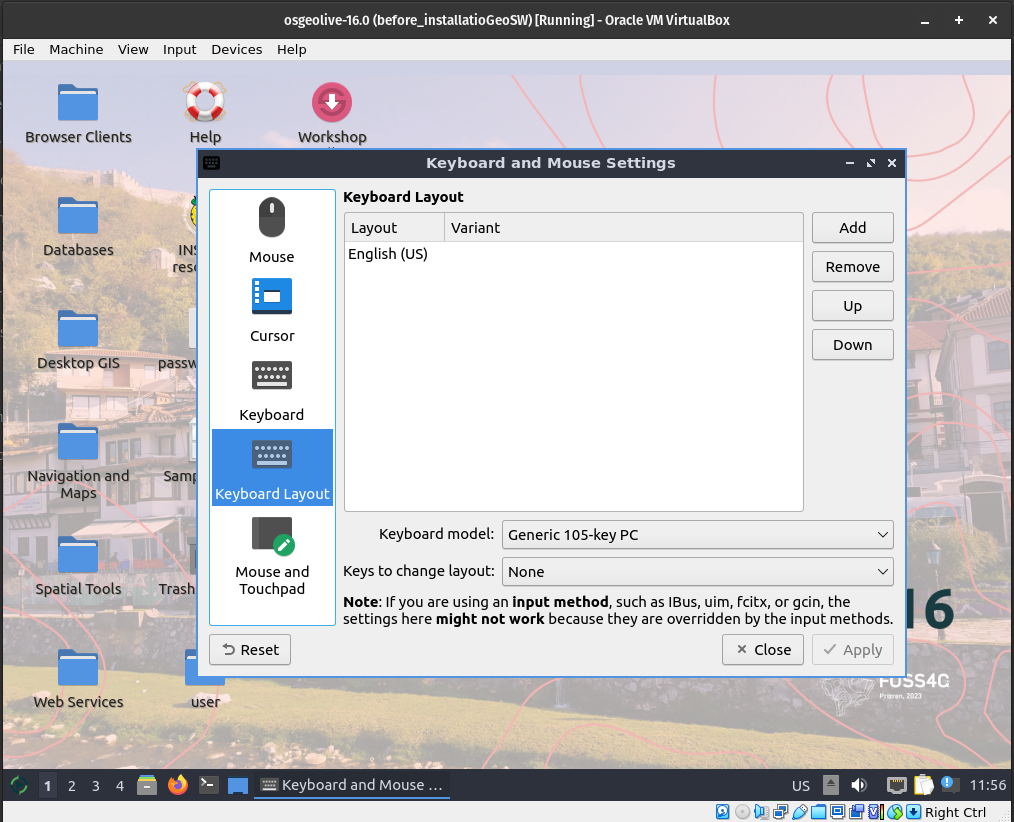
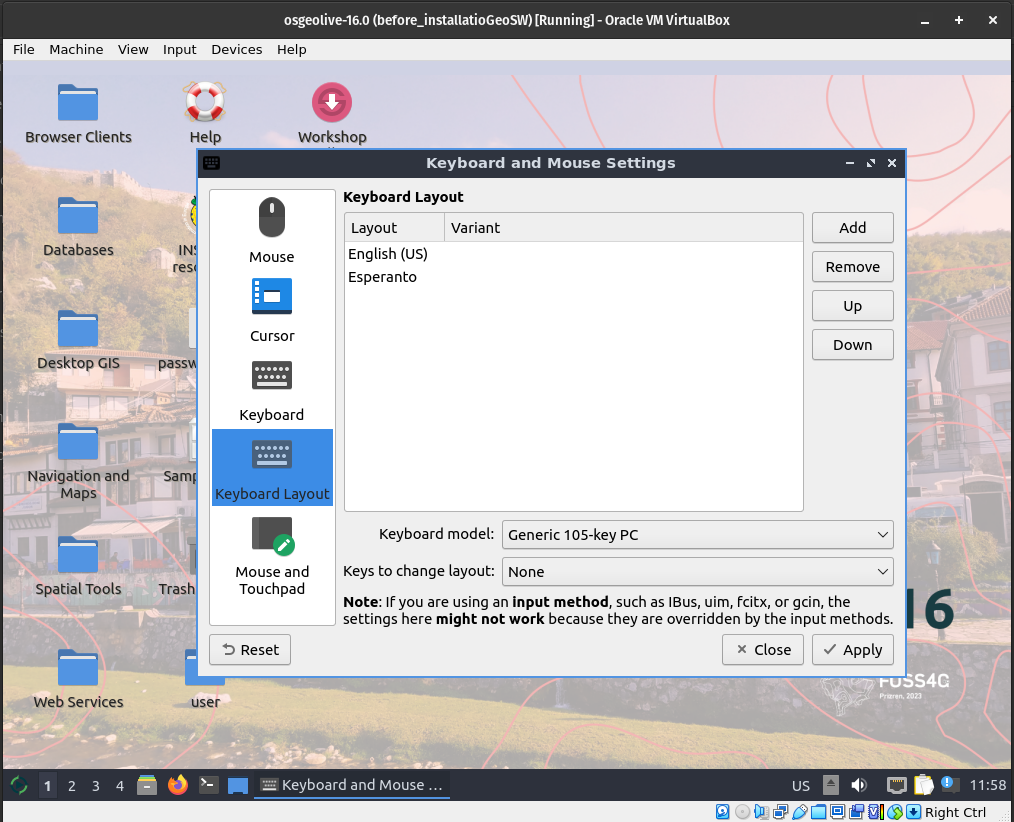
Your keyboard layout will appear as below. Move up to select it as default keyboard layout.
Open the terminal (black icon in the down left corner of the menubar, close to the firefox icon) and test if the keyboard layout is correct.
Update the OS
The first operation after the installation is to run un update of the OS. Therefore, open the bash terminal and run line by line the following codes. The sudo password is “user”. For security what you type is not shown, anyway it is recorded. After typed the password press enter.
Update the OS. This operation can last few minutes. Be patient. If during the installation, some screen pop-up asking some question just accept the default option.
sudo apt update # update the repositories
sudo apt upgrade -y # installation of the sw
sudo apt install linux-generic linux-headers-generic linux-image-generic # install the "The following packages have been kept back:"
sudo apt autoremove -y
Populate OSGeoLive with additional software
Install geo-software
At this point the OSGeoLive Virtual Machine is ready to install additional software and data for running Spatial Ecology courses. In the bash terminal run the following lines
cd /tmp/
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selvaje/SE_data/refs/heads/master/exercise/install_additional_sw_data_4SE_courses.sh
sudo bash ./install_additional_sw_data_4SE_courses.sh
as before the sudo password is user.
Test installed additional software
In the bash terminal run the following lines one by one. Close the window that each time pop-up.
Test pktools
pkfilter --help
You should see the pkfilter manual instructions.
Test OpenEV
source ~/.bashrc
openev /home/user/jupyter/notebook_gallery/Rasterio/data/world.rgb.tif
You should see the openev software popup and open the the tif file.
Git Settings
The below instructions together with the Git Setting for the Spatial Ecology courses YouTube video can guide along the full procedure to retrieve dataset and material for the courses.
We are going to retrieve dataset and material for the first time using git clone.
cd /home/user # enter in user home
git clone https://github.com/selvaje/SE_data # download the data
If the download succeed you should see the SE_data folder
ls -l /home/user/SE_data
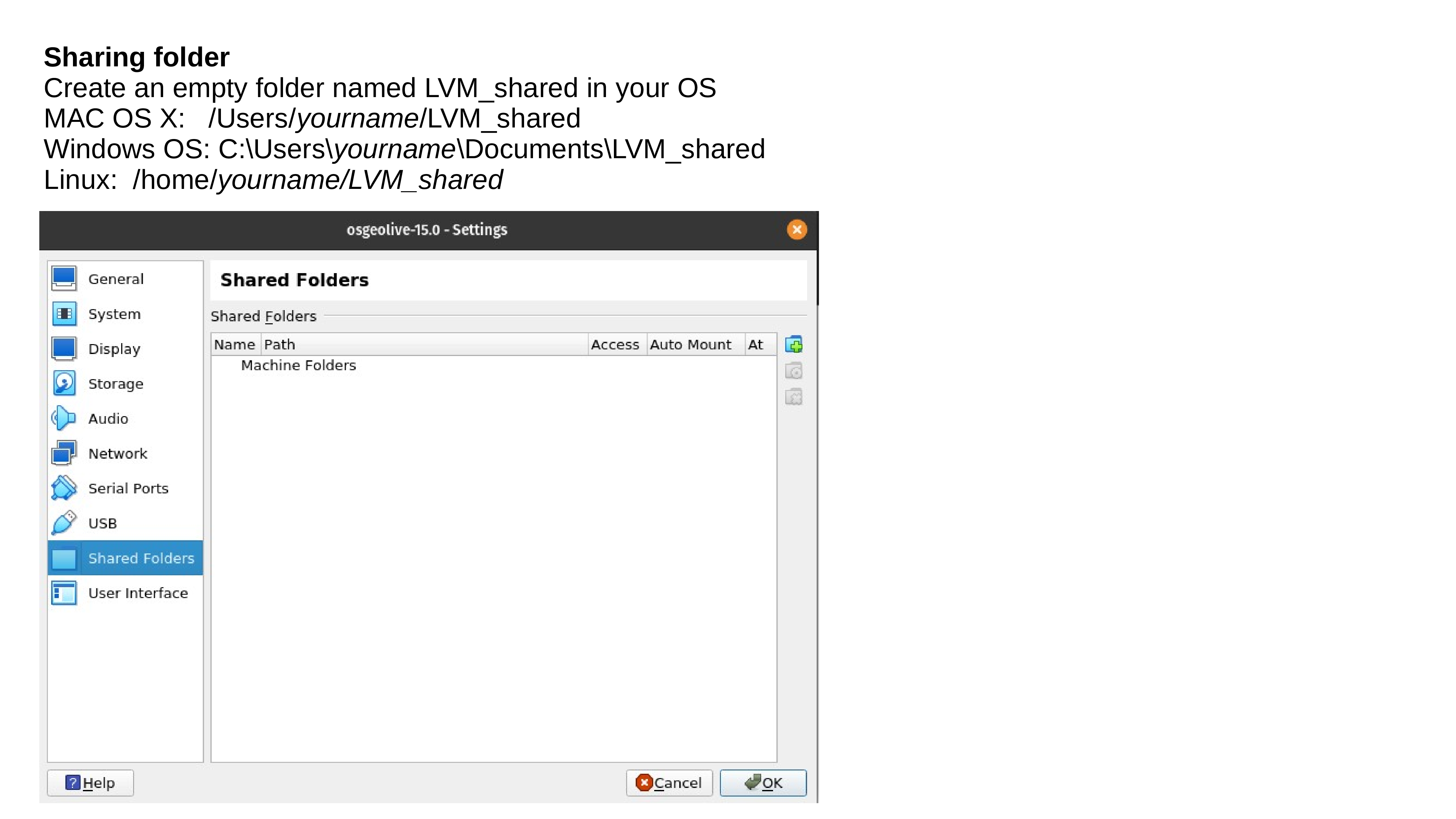
Now we need copy the /home/user/SE_data to an independent directory the:
/media/sf_\LVM_shared/my_SE_data
rsync -hvrPt --ignore-existing ~/SE_data/* /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
cd /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
The /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data is your working directory. Do not touch the ~/SE_data folder!!
Every time that we need to download more data from the git repository, follow this procedure
cd /home/user/SE_data
git pull
rsync -hvrPt --ignore-existing /home/user/SE_data/* /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
cd /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
Now you should be ready to follow the lectures of the Spatial Ecology courses.
Remember always to work on /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
If for any reason the git pull commands give a synchronized error you need to remove the /home/user/SE_data and repeat the git clone and rsync operation.
cd /home/user
rm -ry /home/user/SE_data
git clone https://github.com/selvaje/SE_data
rsync -hvrPt --ignore-existing /home/user/SE_data/* /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
cd /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data
Install jupyter lab
We are going to use jupyter lab as main scripting editor. Here how to install
pip3 install -U jupyterlab
echo "PATH=$PATH:/home/user/.local/bin" >> /home/user/.bashrc
source /home/user/.bashrc
Test jupyter lab
jupyter lab /media/sf_LVM_shared/my_SE_data/exercise/grass_hydro.ipynb
Get familiar with the jupyter lab GUI.